Various sequence to sequence architectures
Basic Models
Sequence to sequence model
x<1> x<2> x<3> x<4> x<5> Jane visite l’Afrique en septembre
y<1> y<2> y<3> y<4> y<5> —> Jane is visiting Africa in September.
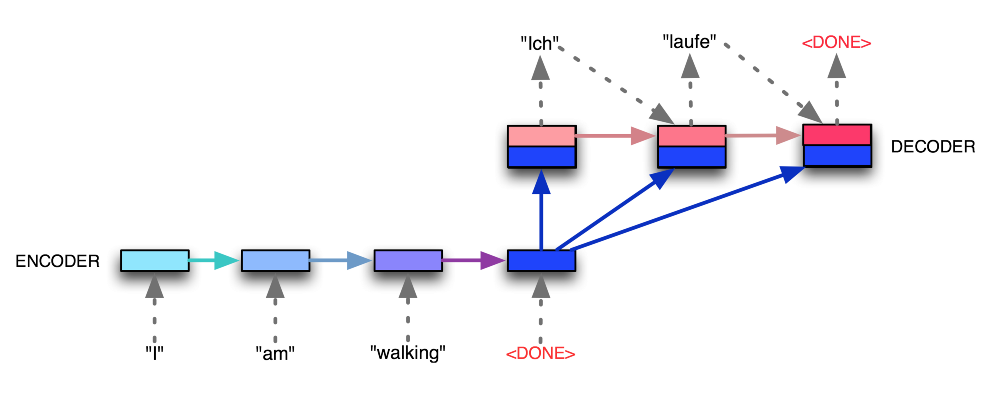
Image captioning
y<1> y<2> y<3> y<4> y<5> y<6> A cat sitting on a chair
Picking the most likely sentence
Machine translation as building a conditional language model
Language model:
Machine translation: decoding network looks just like language model.
(We called it) Conditional language model: Estimate the probability of an English translation conditions on the French input sentence.
Finding the most likely translation
Jane visite l’Afrique en septembre.
—> Jane is visiting Africa in September.
—> Jane is going to be visiting Africa in September.
—> In September, Jane will visit Africa.
—> Her African frient welcomed Jane in September.
argmax P(y<1>,…y
Instead of sampling the outputs at random, we want to find the y that maximizes the term.
Why not a greedy search?
May result in a less optimized output.
Beam Search
Beam search algorithm
B = 3 (beam width)
P(y<1> | x)
P(y<1>, y<2> | x) = P(y<1> | x)P(y<2> | x, y<1>)
P(y<1>, y<2>, y<3> | x) = …
Beam search (B = 3)
in september: a, aaron, … zulu —> jane
jane is: a … zulu —> visiting
jane visits: a … zulu —> africa
When B = 1, similar to greedy search
Refinements to Beam Search
Length Nnormalization
Doing a log on the original function and divide it by 1/(Ty^a)
Beam search discussion
Beam width B? (normal: 10, large: 100, Huge: 1000/3000)
Larger B: better result, slower
Small B: worse result, faster
Unlike exact search algorithms like BFS (Breadth First Search) or DFS (Depth First Search), Beam Search runs faster but is not guaranteed to find exact maximum for arg max_y P(y|x)
Error analysis in beam search
Example Jane visite l’Afrique en septembre.
Human: Jane visits Africa in September. (y*)
Algorithm: Jane visited Africa last September. (yhat)
Use the RNN model to computes P(y*|x) and P(yhat|x) to see which one is larger
- Case 1: P(y*|x) > P(yhat|x)
Beam search chose yhat. But y* attains higher P(y|x).
Conclusion: Beam search is at fault.
- Case 2: P(y*|x) <= P(yhat|x)
y* is a better translation than yhat. But RNN predicted P(y*|x) < P(yhat|x).
Conclusion: RNN model is at fault.
Error analysis process
| Human | Algorithm | P(y*x) | P(yhatx) | At fault? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jane visits Africa in Sep. | Jane visited Africa last Sep. | 2 * e-10 | 1 * e-10 | B |
| … | … | … | … | R |
| … | … | … | … | … |
Bleu Score
Evaluation machine translation French: Le chat est sur le tapis.
Reference 1: The cat is on the mat.
Reference 2: There is a cat on the mat.
Bleu: Bilingual evaluation understudy (Bleu score measure how good is that machine translation)
MT output: the the the the the the the the.
Precision: 7/7 (check if the predition words appears in the reference)
Modified precision: 2/7 (check the appearence up to the maximum)
Bleu score on bigrams Example:
Reference 1: The cat is on the mat.
Reference 2: There is a cat on the mat.
MT output: The cat the cat on the mat.
| Bigrams | Count | Countclip |
|---|---|---|
| the cat | 2 | 1 |
| cat the | 1 | 0 |
| cat on | 1 | 1 |
| on the | 1 | 1 |
| the mat | 1 | 1 |
Bleu score = countclip / count = 4 / 6
Bleu score on unigrams Example:
Reference 1: The cat is on the mat.
Reference 2: There is a cat on the mat.
MT output: The cat the cat on the mat.
P1, Pn(n-gram)
Bleu details Pn = Bleu score on n-grams only
Combined Bleu score: BP exp(1/4 sum(Pn))
where BP = brevity penalty
BP = 1 if MT_output_length > reference_output_length
BP = exp(1 - MT_output_length/reference_output_length) otherwise
Attention Model Intuition
The problem of long sequence
Looking at part of the sentence at a time.
Attention model intuition
Attention Model
Attention model
Computing attention a<t,t’>
a<t,t’> = amount of attention y
Attention examples July 20th 1969 -> 1969 - 07 - 20
23 April, 1564 -> 1564 - 04 - 23
Speech recognition - Audio data
Speech Recognition
Speech recognition problem
audio clip: x -> transcript: y
Attention model for speech recognition
CTC cost for speech recognition
(Connectionist temporal classification)
Basic rule: collapse repeated characters not separated by “blank”
Trigger Word Detection
What is trigger word detection?
Trigger word detection algorithm
Conclusion
Specialization outline
-
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
-
Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter tuning, Regularization and Optimization
-
Structuring Machine Learning Projects
-
Convolutional Neural Networks
-
Sequence Models
blog comments powered by Disqus